Introduction to BCMA

Introduction to BCMA
Firstly, let us see some antibodies.
1. Anti-BCMA-mc-MMAF
This ADC product is composed of an anti-BCMA antibody conjugated via mc linker to MMAF (anti-BCMA-mc-MMAF). It is in Phase I clinical trials and has demonstrated a response in Multiple myeloma (MM) treatment by a MOA (Mechanism of Action) of microtubules depolymerizing.
2.Recombinant Mouse Antibody (J22.9-xi)
Recombinant Mouse Antibody (J22.9-xi) is capable of binding to BCMA, expressed in Chinese Hamster Ovary cells (CHO). The high affinity antibody blocks the binding of the native ligands APRIL and BAFF to BCMA and effectively depletes MM cells in vitro and in vivo and substantially prolongs tumor-free survival under therapeutic conditions in a xenograft mouse model.
What is the BCMA?
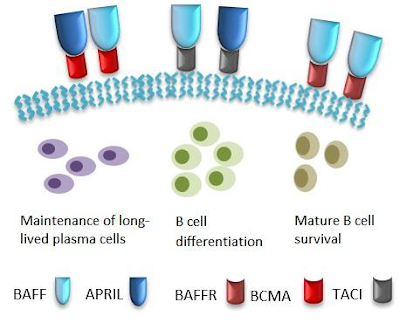
B cell surface maturation antigen (BCMA) is a plasma cell selective protein, which was first found on the surface of mature B lymphocyte and hardly expressed in other tissue cells. It is highly expressed in malignant proliferating B lymphocytes (such as myeloma cells and leukemia cells), and its downstream signaling pathway plays a key role in cell survival, proliferation, metastasis and drug resistance. These characteristics make it a target of immunotherapy for multiple myeloma.
Bioactivity of BCMA
BCMA is a member of the TNF receptor family (NFRSF17), a non-glycosylated type III integrin consisting of 185 amino acid residues. The length of mRNA is 1.2 kb. It plays an important role in managing the maturation of B cells and the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells. In human and mouse BCMA proteins, the N-terminal of BCMA contains a conserved sequence of six cysteines. The hydrophobic analysis and sequence analysis of these conserved regions show that they are similar to the repetitive sequences of six extracellular cysteines of the TNF receptor family, which confirms that BCMA is conservative to some extent. BCMA can not maintain the dynamic balance of normal B cells, but it is necessary for the long-term survival of plasma cells. In multiple myeloma patients, BCMA m RNA is highly expressed in malignant plasma cells.
Ligands of BCMA
APRIL
APRIL, as an important ligand of BCMA, belongs to the TNF (Tumor necrosis factor) receptor family. APRIL has 30% sequence homology with BAFF, another ligand of BCMA, but has higher affinity and interaction with BCMA than APRIL.It consists of 250 amino acids, 28 of which encode intracellular domain, 201 of which encode type II perforating protein and its extracellular domain. In healthy human tissues, its expression is relatively weak, only in monocyte macrophages, activated T lymphocytes, dendritic cells, pancreas and spleen and other tissue cells, but high expression in cancer tissue. APRIL has two forms of bioactivity, soluble in 17 K relative molecular mass and membrane-bound in 30 K relative molecular mass.
APRIL is mainly secreted by osteoclasts and can directly promote the survival of malignant plasma cells through proteoglycan. When BCMA is combined with BCMA, the viability of bone marrow blood cells and plasma mother cells is enhanced, and key immune checkpoint molecules can be directly up-regulated to create an immunosuppressed bone marrow microenvironment. This binding process can also induce classical and non-classical NF-KB pathways, further increase the production of angiogenesis and transfer factors, adhesion and migration molecules, and growth and survival genes.
BAFF
BAFF, also known as BLys, is a member of the TNF family. It is a type II transmembrane protein composed of 285 amino acids with a relative molecular weight of 31.3 K. There are two forms of membrane binding and soluble proteins, which are expressed mainly by innate immune cells, such as monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells. BAFF binds BCMA with relatively low affinity, and BAFF can also connect to two other members of the TNF receptor family: B cell activating factor receptor (BAFF-R), transmembrane activator and calmodulin ligand interaction molecule (TACI).
Immunotherapy targeting BCMA
In recent years, new immunotherapy methods for BCMA tumors have become more and more mature, mainly including CAR-T (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T.Cell Immunotherapy), Bispecific antibody (BsAb) and anti-body-drug coupling (ADC) three camps.
CAR-T
Using different costimulatory regions to optimize the design of CAR and to target different or multiple B cell antigens of CAR are the solutions to the problems faced by researchers in CAR-T therapy. At present, the research of CAR-T therapy for multiple myeloma targeting BCMA is in its infancy, but the results of clinical trials have shown gratifying results. The key to break through this technology is the problems it faces, such as cytokine storm and high recurrence rate. We believe that CAR-T drugs targeting BCMA will be available soon.
BsAb
Bispecific antibody is a new second generation antibody. It either contains two antigen binding sites or can target effector cells. It can block signal transduction triggered by two independent antigens or recruit effector cells to the vicinity of cancer cells by the interaction between target cells and functional cells, thereby enhancing the killing function of cancer cells.
At present, although the research progress of bispecific antibodies is slow, pharmaceutical giants continue to add codes and new drugs to the market, which promotes the prosperity of the industry. Different from traditional antibodies, it can bind two different antigens or epitopes, so its most widely used is cancer immunotherapy. The research of BCMA-targeted bispecific antibodies for multiple myeloma is also under way.
ADC
Of course, in addition to BCMA CAR-T immunotherapy, different types of drugs from other companies follow. It is worth noting that BCMA ADC is also in the clinical stage.
To sum up, CAR-T therapy, ADC drugs and bispecific antibody drugs targeting BCMA all show the hope of treating multiple myeloma, indicating that BCMA is a target worthy of cultivation by medical giants.
Three new immunotherapies have shown good results in pre-clinical and clinical trials, especially in the highly focused CAR-T therapy. In just a few decades, conceptual gene therapy has become a practical program. CAR can recognize tumor antigens independently of MHC, and has the characteristics of costimulatory domain which can effectively enhance T cell proliferation. It has far-reaching significance for the clinical treatment of multiple myeloma. The development of BCMA-related ligand BAFF blockers to block the interaction between BAFF and BCMA, or to prevent the transmission of proliferation signals through signal pathway blockers, has gradually jumped into the new ideas of medical workers considering the treatment of multiple myeloma. It is believed that there will be more targeted BCMA drugs in the near future, so as to open up a new way of immunotherapy for multiple myeloma.